Neonatology
Neonatology is a subspecialty of pediatrics that focuses on the care of newborn infants, especially those who are born prematurely, have low birth weight, or have medical conditions that require specialized care. Neonatologists are pediatricians who have additional training in the care of newborn infants.
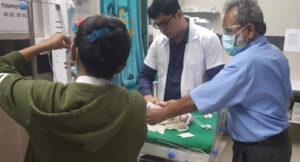
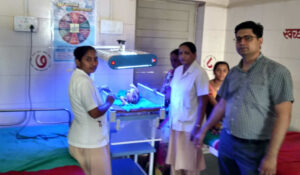
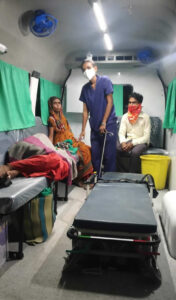
Neonatology is a highly specialized field that requires a deep understanding of the unique medical needs of newborns. Neonatologists work in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) where they provide medical care to premature and critically ill infants. They are trained to manage a range of medical conditions, including respiratory distress syndrome, apnea, hypotension, sepsis, and jaundice.
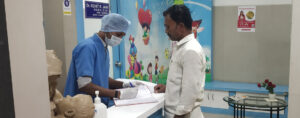
In addition to providing medical care, neonatologists also work closely with families to provide emotional support and education on caring for their newborn. They help families understand their infant’s medical condition and treatment options, and they provide guidance on feeding, bonding, and other important aspects of newborn care.
Neonatology
Neonatology is an important field of medicine that has helped to improve the survival rates and overall health outcomes for premature and critically ill infants. Advances in neonatal care, including improvements in technology and treatment strategies, have led to better outcomes for these vulnerable infants.
Frequently Ask Questions (FAQ) -
Do you have questions about Neonatology treatment? We’re here to help! Check out the answers to some of most frequently asked questions.
What is rehydration therapy for diarrhea?
Why is rehydration therapy important for children with diarrhea?
What are the signs of dehydration in a child with diarrhea?
What fluids are used for rehydration therapy?
How should I give oral rehydration solution to my child?
When should I seek medical attention for my child with diarrhea?
Can I use homemade solutions like salt and sugar water instead of ORS?
How long should I continue rehydration therapy?
Are there any additional measures to manage diarrhea in children?
How can I prevent diarrhea in children?
Every baby’s life is precious, and they deserve the very best chance in life. Dr. Rohit Jain and team are highly trained neonatologists to provide the best possible care for babies requiring intensive care and monitoring after birth. At Neolife dental and children hospital, we offer compassionate care for your child. Please feel free to contact us to schedule an appointment!