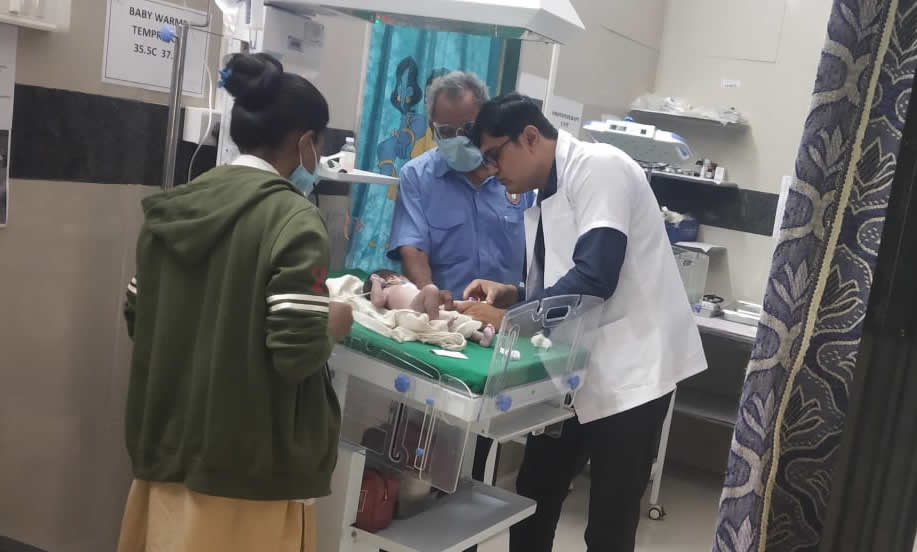
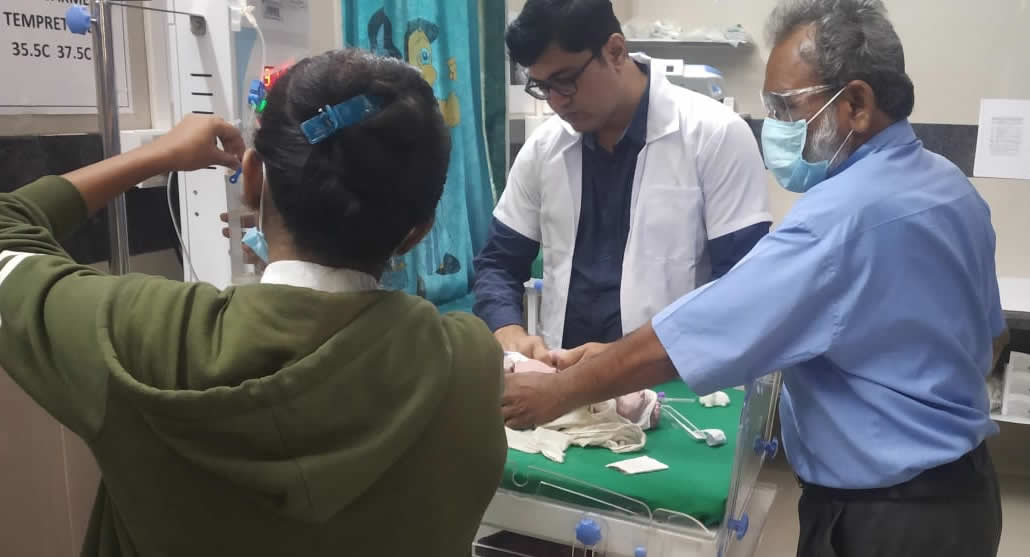
Trauma Care Centre At Aurangabad
Children who have experienced trauma require specialized care to help them heal and recover. Traumatic experiences can have a significant impact on a child’s emotional, psychological, and physical well-being.
Here are some essential aspects of trauma care for children:
Safety and Stability: Creating a safe and stable environment is crucial for traumatized children. This includes ensuring their physical safety, providing a predictable routine, and establishing a secure and nurturing atmosphere.
Trauma-Informed Approach: Professionals working with traumatized children should adopt a trauma-informed approach. This involves understanding the effects of trauma, recognizing trauma triggers, and responding to children with empathy and sensitivity.
Mental Health Support: Trauma often leads to mental health challenges such as anxiety, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), or behavioral issues. Access to mental health services, including therapy and counseling, is vital for children to address these issues.
Play Therapy: Play therapy is a commonly used intervention for traumatized children. Through play, children can express their feelings, process their experiences, and learn coping strategies in a safe and non-threatening environment.
Education and Support for Caregivers: Traumatized children benefit from having supportive and well-informed caregivers. Providing education and guidance to parents, guardians, and other caregivers can help them understand the impact of trauma and learn effective strategies to support the child’s recovery.
Collaborative Approach: Effective trauma care for children involves collaboration among different professionals, including therapists, counselors, teachers, and medical providers. Working together as a team ensures a comprehensive and coordinated approach to the child’s care.
Trauma-Specific Interventions: Evidence-based trauma interventions tailored to the child’s age and developmental stage are crucial. These may include trauma-focused cognitive-behavioral therapy (TF-CBT), eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), or other specialized interventions designed to address trauma-related symptoms.
Supportive Services: Children who have experienced trauma may require additional supportive services, such as academic assistance, access to healthcare, and assistance with basic needs. Collaborating with community resources and social service agencies can help ensure the child’s comprehensive well-being.
Trauma Prevention and Awareness: Raising awareness about trauma and its impact on children is essential for prevention and early intervention. Educating communities, schools, and professionals about trauma-informed practices can help create a supportive environment for children and reduce the likelihood of further trauma.
Long-Term Support: Trauma recovery is a journey that may require ongoing support. It is important to provide follow-up care and monitor the child’s progress even after the initial intervention. This can help identify any ongoing needs or potential setbacks and ensure continued healing.
Trauma Care Centre
Remember that each child’s experience and response to trauma is unique, and the care provided should be tailored to their individual needs. Professional guidance from trained trauma specialists is crucial in providing effective care for traumatized children.
There are several reasons why a child may experience frequent fractures (also known as broken bones). Some of the common factors that can contribute to this are:
Accidental Injuries: Children are naturally active and curious, which can sometimes lead to accidental falls, collisions, or other mishaps that result in fractures. Their developing coordination and motor skills may make them more prone to accidents, especially during activities such as sports or playing on playgrounds.
Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Osteogenesis Imperfecta (OI), also known as brittle bone disease, is a genetic disorder that affects the production of collagen, a protein that provides strength and structure to bones. Children with OI have fragile bones that can break easily, even with minimal force or trauma.
Vitamin D Deficiency: Vitamin D is essential for the proper absorption of calcium and the development of strong bones. Insufficient vitamin D levels can lead to weakened bones, making children more susceptible to fractures.
Calcium and Mineral Deficiencies: Inadequate intake of calcium and other essential minerals, such as phosphorus, can weaken bone density and increase the risk of fractures.
Certain Medical Conditions: Some medical conditions, such as osteoporosis (a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones), cancer, or bone tumors, can increase the likelihood of fractures in children.
Repetitive Stress Injuries: Repetitive stress or overuse injuries can occur when a child repeatedly performs certain activities or sports that put excessive strain on the bones. Examples include stress fractures in athletes or dancers who engage in intense training or activities that involve repetitive impacts.
Child Abuse: Unfortunately, child abuse can also be a cause of frequent fractures in children. Non-accidental injuries or physical abuse can lead to multiple fractures in different stages of healing, which may indicate a pattern of abuse.
It’s important to note that frequent fractures in children should always be evaluated by a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and provide appropriate treatment and support.
Frequently Ask Questions (FAQ) -
Do you have questions about Trauma Care Centre? We’re here to help! Check out the answers to some of most frequently asked questions.
Why did this happen to me?
Will I be safe now?
Is it okay to feel this way?
Can I trust people again?
Will things go back to how they were before?
Why do I have nightmares or flashbacks?
Am I to blame for what happened?
Can I talk about what happened?
Will I ever feel normal again?
Who can I turn to for help?
A body wound or shock produced by sudden physical injury, as from violence or accident. We provide comprehensive care for all our patients. At Neolife Dental and Children Hospital in Chatrapati Shambhajinagar, We offer trauma care for those who need a longer period of time to recover from a severe injury.
Please feel free to contact us to schedule an appointment!